Geriatric/Old age care
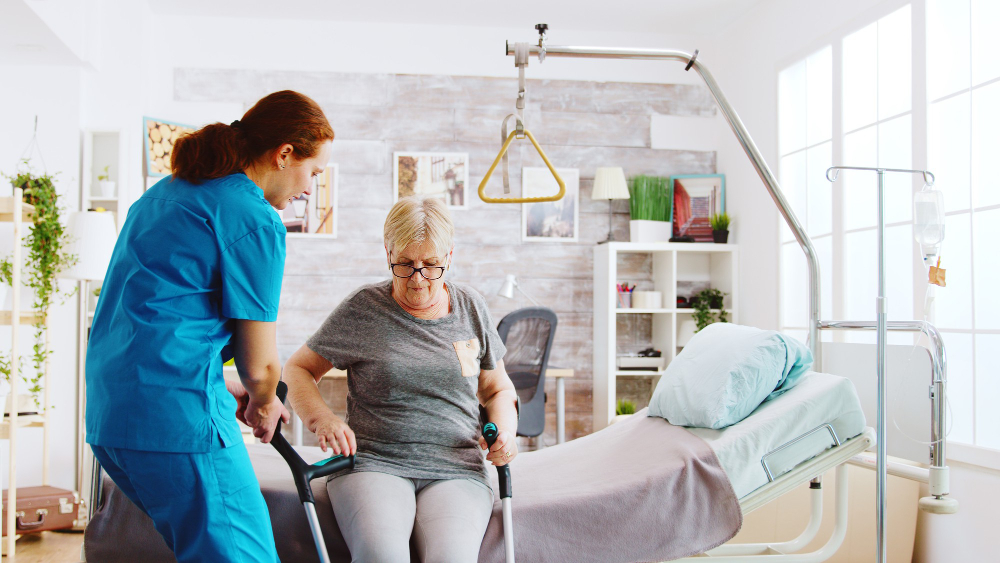

- Geriatric or old age care focuses on meeting the unique needs and challenges of elderly individuals as they age.
- It encompasses a holistic approach to physical, mental, and social well-being, considering factors such as chronic illnesses, functional limitations, and psychosocial aspects.
- Assessment of geriatric patients involves evaluating medical history, functional status, cognitive function, and social support systems.
- Preventive care plays a crucial role in maintaining health and independence among the elderly, including regular health screenings, vaccinations, and fall prevention measures.
- Management of chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, osteoarthritis, and dementia requires careful monitoring, medication management, and lifestyle interventions.
- Multidisciplinary care teams, including physicians, nurses, social workers, physical and occupational therapists, and geriatric specialists, collaborate to provide comprehensive care.
- Palliative and end-of-life care addresses the unique needs of elderly patients with advanced illnesses, focusing on symptom management, comfort, and quality of life.
- Nutritional support ensures adequate dietary intake, addressing issues such as malnutrition, dehydration, and swallowing difficulties.
- Functional rehabilitation programs aim to improve mobility, strength, and activities of daily living through physical therapy, occupational therapy, and assistive devices.
- Cognitive stimulation activities and social engagement programs promote mental well-being, prevent isolation, and enhance cognitive function.
- Home-based care services provide assistance with activities of daily living, medication management, and monitoring of health status for elderly individuals who prefer to age in place.
- Residential care options, including assisted living facilities and nursing homes, offer 24-hour supervision, medical care, and support services for older adults with complex needs.
- Family involvement and caregiver support are integral to geriatric care, providing emotional support, respite care, and assistance with decision-making.
- Advocacy for policies and programs that promote healthy aging, access to healthcare, and social inclusion is important for addressing the needs of elderly populations.
- Overall, geriatric care aims to optimize health, independence, and quality of life for older adults, enabling them to age with dignity and purpose.