Arthritis/Joints Pain
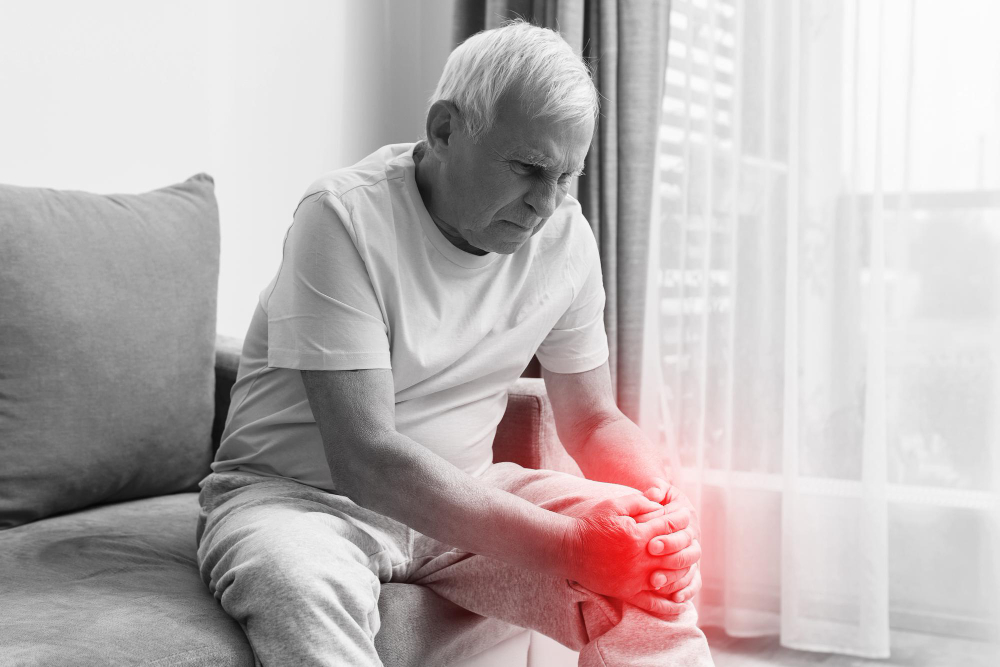

- Arthritis is a group of conditions characterized by inflammation and damage to the joints.
- Common types include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout.
- Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion.
- Risk factors include age, genetics, obesity, joint injuries, and autoimmune diseases.
- Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, imaging tests like X-rays or MRI, and blood tests.
- Treatment aims to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, preserve joint function, and improve quality of life.
- Medications such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are often prescribed.
- Physical therapy helps strengthen muscles around the joints, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Assistive devices like braces, splints, or orthotics may provide support and alleviate strain on affected joints.
- Lifestyle modifications such as weight management, regular exercise, and joint protection techniques are essential.
- In severe cases, surgical options like joint replacement or arthroplasty may be considered.
- Complementary therapies like acupuncture, massage, or dietary supplements may offer additional relief.
- Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is crucial to assess disease progression and adjust treatment accordingly.
- Arthritis management requires a multidisciplinary approach involving rheumatologists, orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals.
- While arthritis is a chronic condition, proactive management can help individuals lead active and fulfilling lives while minimizing pain and disability.