Lumbar Spondylosis
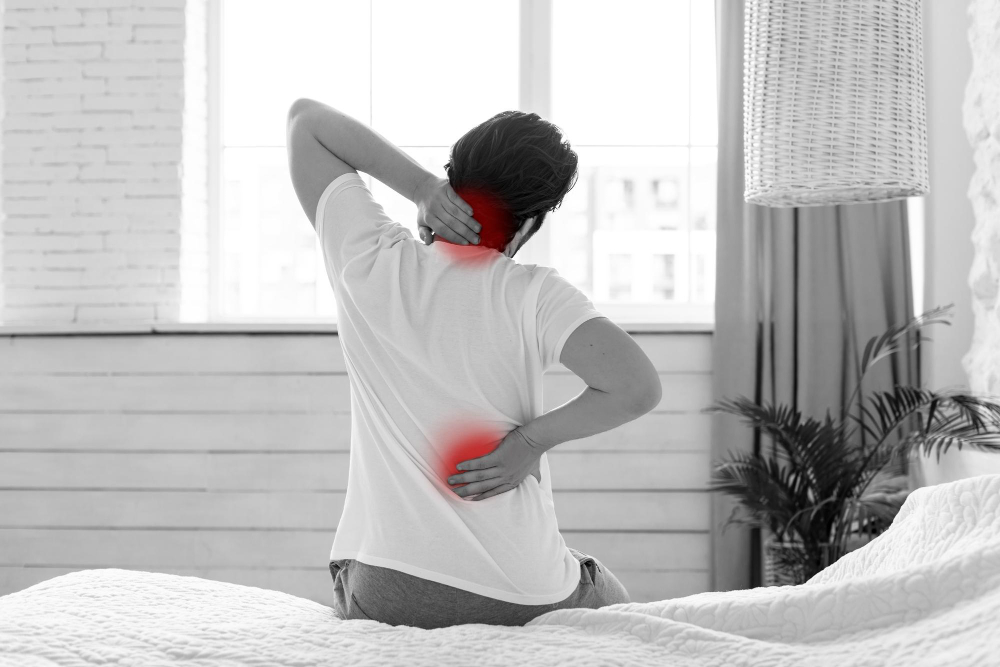

- Lumbar Spondylosis refers to degenerative changes in the lower back, particularly in the lumbar spine region.
- It involves wear and tear on the intervertebral discs, vertebrae, and associated structures in the lumbar spine.
- Common symptoms include lower back pain, stiffness, and decreased flexibility, especially after prolonged sitting or standing.
- Pain may radiate to the buttocks, thighs, or legs, often due to nerve compression or irritation.
- Risk factors include aging, genetics, repetitive stress, obesity, and sedentary lifestyle.
- Diagnosis typically involves medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans.
- Treatment aims to manage symptoms, improve function, and prevent further degeneration.
- Conservative approaches include rest, physical therapy, exercise, and pain management medications.
- In severe cases or when conservative measures fail, surgical options like spinal fusion or decompression may be considered.
- Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and regular exercise can help alleviate symptoms and prevent progression.
- Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is crucial for monitoring the condition, adjusting treatment as needed, and maximizing quality of life.
- While Lumbar Spondylosis is a chronic condition, proactive management strategies can significantly improve outcomes and overall well-being.