Cervical Spondylosis
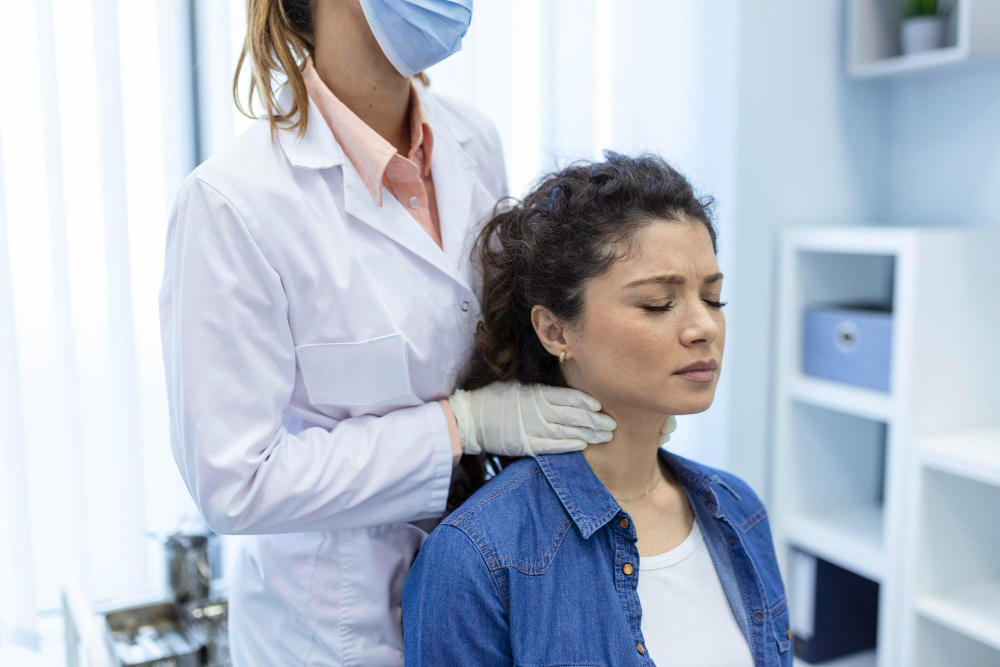
- Cervical Spondylosis, also known as neck arthritis, is a degenerative condition affecting the cervical spine in the neck region.
- It results from age-related changes, including disc degeneration, bone spurs, and loss of cartilage.
- Common symptoms include neck pain, stiffness, headaches, and numbness or tingling in the arms or hands.
- Risk factors include aging, previous neck injuries, poor posture, and genetic predisposition.
- Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, and nerve studies.
- Treatment aims to manage symptoms, improve function, and prevent complications.
- Conservative treatments include rest, physical therapy, exercise, and pain management medications.
- Neck exercises can help strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain.
- Neck braces or cervical collars may provide support and restrict movement during the healing process.
- In severe cases or when conservative measures fail, surgical options like cervical fusion or decompression may be considered.
- Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining good posture, avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, and using ergonomic equipment are essential.
- Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is crucial for monitoring the condition, adjusting treatment as needed, and preventing further complications.
- While cervical spondylosis is a chronic condition, proactive management strategies can significantly improve outcomes and overall well-being.
- Education about proper posture, body mechanics, and self-care techniques is important for long-term management and prevention of recurrence.
- Early intervention and comprehensive treatment approaches can help individuals maintain mobility, reduce pain, and enhance quality of life.