Electrotherapy
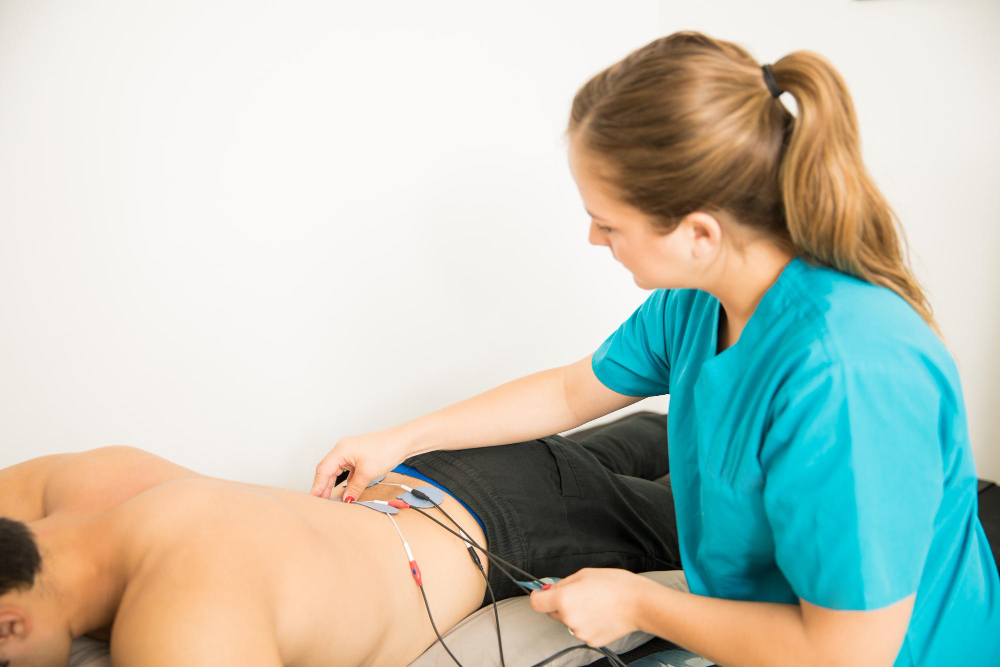
- Electrotherapy is a therapeutic technique that utilizes electrical stimulation for various medical purposes.
- It involves the application of controlled electrical currents to stimulate nerves, muscles, and other tissues to alleviate pain, promote healing, and restore function.
- One common application is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), which uses low-voltage electrical currents to relieve pain by disrupting pain signals sent to the brain.
- Another technique is neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), which targets specific muscles to improve strength, reduce spasticity, and enhance motor control, commonly used in rehabilitation settings.
- Electrical stimulation can also be employed for wound healing purposes, such as in high-voltage pulsed current (HVPC) therapy, which enhances tissue repair and reduces inflammation.
- Electrotherapy has been found effective in treating various conditions including musculoskeletal injuries, chronic pain syndromes, neurological disorders, and wound healing.
- It can be administered through various modalities including electrodes placed on the skin, specialized devices, or implants.
- Electrotherapy sessions are typically supervised by trained healthcare professionals to ensure safety and efficacy.
- While generally considered safe, electrotherapy may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or implants, and its effectiveness can vary depending on factors such as the type and severity of the condition being treated.