Exercise therapy
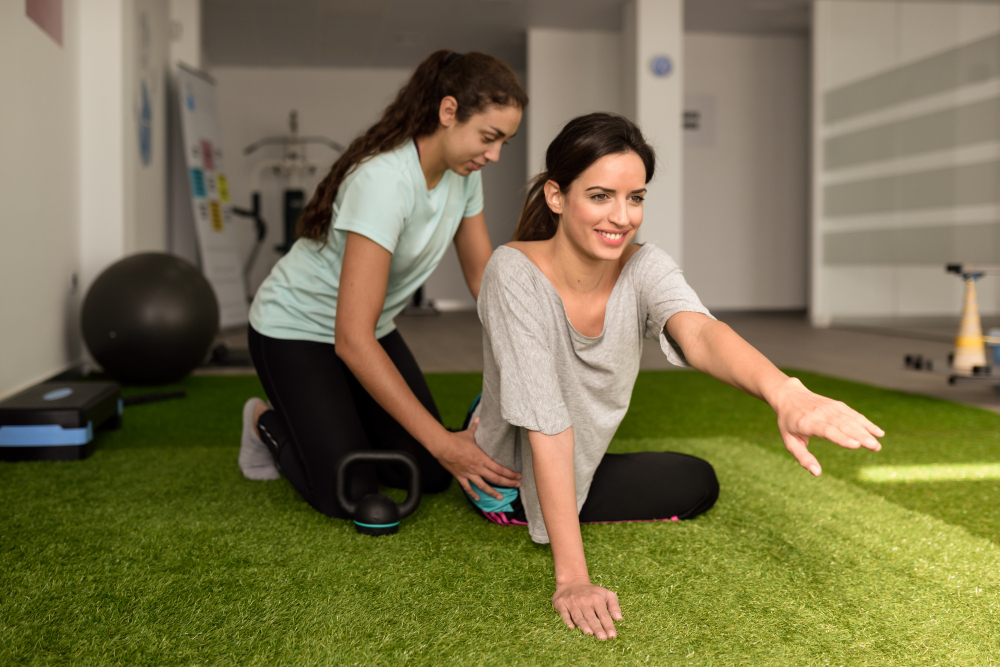

- Exercise therapy, also known as therapeutic exercise or physiotherapy, involves the use of physical activity to improve, restore, or maintain physical function and overall health.
- It is often prescribed by healthcare professionals such as physiotherapists, chiropractors, or sports medicine specialists to address a wide range of conditions, injuries, or disabilities.
- The goals of exercise therapy include reducing pain, improving flexibility, strength, balance, coordination, and endurance.
- Exercise therapy can be tailored to the individual’s needs and abilities, taking into account factors such as age, fitness level, medical history, and specific health goals.
- It encompasses various forms of exercise, including aerobic exercises (e.g., walking, swimming), resistance training (e.g., weightlifting, resistance bands), flexibility exercises (e.g., stretching, yoga), and balance exercises (e.g., tai chi, stability exercises).
- Progression in exercise therapy is typically gradual, with adjustments made based on the individual’s response and progress.
- Regular adherence to an exercise therapy program is essential for optimal results, often requiring a combination of supervised sessions and home exercises.
- Research has shown that exercise therapy can be effective in managing chronic conditions such as arthritis, back pain, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity.
- Additionally, exercise therapy can play a crucial role in injury prevention, rehabilitation post-injury or surgery, and enhancing overall quality of life.